Chemical energy
Chemical energy is the potential of a chemical substance to undergo a transformation through a chemical reaction or, to transform other chemical substances. Breaking or making of chemical bonds involves energy, which may be either absorbed or evolved from a chemical system. Energy that can be released (or absorbed) because of a reaction between a set of chemical substances is equal to the difference between the energy content of the products and the reactants. This change in energy is called the change in internal energy of a chemical reaction. Where 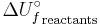 is the internal energy of formation of the reactant molecules that can be calculated from the bond energies of the various chemical bonds of the molecules under consideration and
is the internal energy of formation of the reactant molecules that can be calculated from the bond energies of the various chemical bonds of the molecules under consideration and 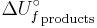 is the internal energy of formation of the product molecules. The internal energy change of a process is equal to the heat change if it is measured under conditions of constant volume, as in a closed rigid container such as a bomb calorimeter. However, under conditions of constant pressure, as in reactions in vessels open to the atmosphere, the measured heat change is not always equal to the internal energy change, because pressure-volume work also releases or absorbs energy. (The heat change at constant pressure is called the enthalpy change; in this case the enthalpy of formation).
is the internal energy of formation of the product molecules. The internal energy change of a process is equal to the heat change if it is measured under conditions of constant volume, as in a closed rigid container such as a bomb calorimeter. However, under conditions of constant pressure, as in reactions in vessels open to the atmosphere, the measured heat change is not always equal to the internal energy change, because pressure-volume work also releases or absorbs energy. (The heat change at constant pressure is called the enthalpy change; in this case the enthalpy of formation).
Another useful term is the heat of combustion, which is the energy released due to a combustion reaction and often applied in the study of fuels. Food is similar to hydrocarbon fuel and carbohydrate fuels, and when it is oxidized, its caloric content is similar (though not assessed in the same way as a hydrocarbon fuel — see food energy).
In chemical thermodynamics the term used for the chemical potential energy is chemical potential, and for chemical transformation an equation most often used is the Gibbs-Duhem equation.